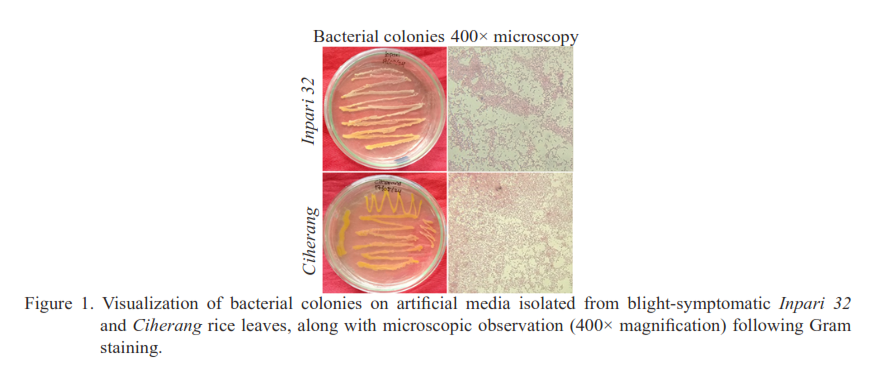
Visual observation and image analysis method of blight disease severity for resistance assessment of two rice varieties
Main Article Content
Abstract
Bacterial Leaf Blight (BLB), caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, is a major threat to global rice production, causing yield losses of up to 80%. Accurate assessment of disease severity is essential for developing resistant rice varieties and implementing effective management strategies. However, traditional visual observation methods, while widely used, are prone to subjectivity and reduced accuracy. This study evaluates the accuracy of image analysis for assessing rice plant resistance to BLB. Disease severity was assessed using both visual observation and image analysis, with results quantified through the Area Under the Disease Progress Curve (AUDPC) and infection rate calculations. Image analysis outperformed visual observation, achieving an accuracy rate above 96%, compared to less than 90% for the latter. The Ciherang variety demonstrated greater resistance to BLB, with lower AUDPC and infection rates when assessed using image analysis. Conversely, visual observation produced contradictory results, highlighting its limitations. This study concludes that image analysis provides a more objective, reproducible, and accurate approach to assessing disease severity, with implications for breeding programs and integrated disease management systems. Further research is recommended to validate these methods across a broader range of rice genotypes and environmental conditions.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Acharya A, Adhikari NR, Amgain RB, Poudel A, Yadav R, & Poudyal K. 2018. Identification of rice genotypes resistant to bacterial leaf blight disease using SSR markers. J. Inst. Agric. Anim. Sci. 35(1): 113–120. https://doi.org/10.3126/jiaas.v35i1.22521
Ahmad TM, Haider MS, Randhir TO, Randhir R, & Ahmad SR. 2023. Spatial analysis of factors influencing bacterial leaf blight in rice production. Braz. J. Biol. 83: e264249. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.264249
Askey BC, Dai R, Lee WS, & Kim J. 2019. A noninvasive, machine learning–based method for monitoring anthocyanin accumulation in plants using digital color imaging. Appl. Plant Sci. 7(11): e11301. https://doi.org/10.1002/aps3.11301
Bae N, Park HJ, Park H, Kim M, Do E, & Han SW. 2018. Elucidating functions of FleQ in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae by comparative proteomic and phenotypic analyses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(10): 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103038
Bande LOS & Hasan A. 2024. Estimation of blight and spot diseases severity in Ciherang and Ciliwung rice varieties based on vegetation index algorithms. Biodiversitas. 25(3): 1015–1021. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d250314
Barbedo JGA. 2013. Digital image processing techniques for detecting, quantifying and classifying plant diseases. SpringerPlus. 2(1): 660. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-660
Bock CH, Chiang KS, & Del Ponte EM. 2021. Plant disease severity estimated visually: A century of research, best practices, and opportunities for improving methods and practices to maximize accuracy. Trop. Plant Pathol. 47: 25–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-021-00439-z
Bock CH, Poole GH, Parker PE, & Gottwald TR. 2010. Plant disease severity estimated visually, by digital photography and image analysis, and by hyperspectral imaging. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 29(2): 59–107. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352681003617285
Farvardin A, González-Hernández AI, Llorens E, Camañes G, Scalschi L, & Vicedo B. 2024. The dual role of antimicrobial proteins and peptides: Exploring their direct impact and plant defense-enhancing abilities. Plants. 13(15): 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13152059
Febriyanto DW, Nurtiati N, Mugiastuti E, Manan A, Sastyawan MWR, & Soesanto L. 2022. Application of three weed pathogenic fungi on bok choy (Brassica rapa subsp. chinnensis). Biosaintifika. 14(3): 408–416. https://doi.org/10.15294/biosaintifika.v14i3.37319
Fontyn C, Meyer KJ, Boixel AL, Delestre G, Piaget E, Picard C, Suffert F, Marcel TC, & Goyeau H. 2023. Evolution within a given virulence phenotype (pathotype) is driven by changes in aggressiveness: A case study of French wheat leaf rust populations. Peer Community J. 3: e39. https://doi.org/10.24072/pcjournal.264
Goriewa-Duba K, Duba A, Wachowska U, & Wiwart M. 2018. An evaluation of the variation in the morphometric parameters of grain of six Triticum species with the use of digital image analysis. Agronomy. 8(12): 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8120296
Haidary MN, Tamura T, & Ueno M. 2018. Inhibitory activity of Paenibacillus sp. isolated from soil in Gotsu City, Shimane Prefecture, against Xanthomas oryzae pv. oryzae, the causal agent of rice bacterial leaf blight. Adv. Microbiol. 8(3): 197–210. https://doi.org/10.4236/aim.2018.83014
Hasan A, Widodo, Mutaqin KH, Hidayat SH, & Taufik M. 2021. Quantitative assessment of mosaic disease severity based on digital image processing. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 694: 012043. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/694/1/012043
Hassan Z, Shahbaz B, Ali A, Gilani SKH, & Khan MAA. 2023. Assessing the knowledge, attitude, and skills of plant doctors towards plant health clinics in Pakistan. J. Plant Environ. 5(1): 15–22. https://doi.org/10.33687/jpe.005.01.4607
Hongo C, Takahashi Y, Sigit G, Utoyo B, & Tamura E. 2022. Advanced damage assessment method for bacterial leaf blight disease in rice by integrating remote sensing data for agricultural insurance. J Agric Sci. 14(4): 1–18. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v14n4p1
Iqbal M, Javed N, Shahid M, Ali S, & Arshad M. 2022. Effect of sowing times and rice varietal resistance on the severity of narrow brown leaf spot disease in relation to environmental conditions. Int J Phytopathol. 11(3): 215–225. https://doi.org/10.33687/phytopath.011.03.4352
Jiang S, He M, Xiang XW, Adnan M, & Cui ZN. 2019. Novel S-Thiazol-2-yl-furan-2-carbothioate derivatives as potential T3SS inhibitors against Xanthomonas oryzae on rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 67(43): 11867–11876. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04085
Jiang N, Yan J, Liang Y, Shi Y, He Z, Wu Y, Zeng Q, Liu X, & Peng J. 2020. Resistance genes and their interactions with bacterial blight/leaf streak pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in rice (Oryza sativa L.) - an updated review. Rice. 13(1): 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y
Jiang D, Zhang D, Li S, Liang Y, Zhang Q, Qin X, Gao J, & Qiu J. 2022. Highly efficient genome editing in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae through repurposing the endogenous type I?C CRISPR?Cas system. Mol Plant Pathol. 23(4): 583–594. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.13178
Jirankali JP, Deepak CA, Chethana BS, Sandesh GM, Nikhil G, & Rajanna MP. 2023. Screening of rice genotypes for resistance against bacterial blight disease. Int. J. Econ Plants. 10(4): 268–274. https://doi.org/10.23910/2/2023.4882a
Khaeruni A & Wijayanto T. 2013. Pathotype grouping of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae isolates from South Sulawesi and Southeast Sulawesi. AGRIVITA J. Agric. Sci. 35(2): 138–144. https://doi.org/10.17503/Agrivita-2013-35-2-p138-144
Kim SM & Reinke RF. 2019. A novel resistance gene for bacterial blight in rice, Xa43(t) identified by GWAS, confirmed by QTL mapping using a bi-parental population. PLoS ONE. 14(2): e0211775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211775
Kim SI, Kwak JS, Song JT, & Seo HS. 2016. Long-term effect of niclosamide on inhibition of bacterial leaf blight in rice. J. Plant Prot. Res. 56(4): 323–327. https://doi.org/10.1515/jppr-2016-0051
Lestari D, Prasetyawati ET, & Suryaminarsih P. 2023. Modelling intensity of bacterial leaf blight on rice plants due to influence of abiotic factors in Babaksari Village, Gresik. Agric. 35(1): 149–158. https://doi.org/10.24246/agric.2023.v35.i1.p149-158
Long X, Zhang G, Long H, Wang Q, Wang C, Zhu M, Wang W, Li C, Wang Z, & Ouyang G. 2023. Discovery and mechanism of Novel 7-Aliphatic Amine Tryptanthrin derivatives against phytopathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(13): 10900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310900
Liu Y, Yuan X, Yang H, Huang J, Zhu Z, Lu D, Shen S, Yang Y, & Rao Y. 2024. Genetic dissection of rice resistance to bacterial blight. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 40(4): 1040–1049. https://doi.org/10.13345/j.cjb.230789
Madden LV, Hughes G, & van den Bosch F. 2017. Temporal analysis I: Quantifying and comparing epidemics. In: Madden LV, Hughes G, & van den Bosch F (Eds.). The Study of Plant Disease Epidemics. pp. 63–116. The American Phytopathological Society. St. Paul. Minnesota. https://doi.org/10.1094/9780890545058.004
Méline V, Caldwell DL, Kim BS, Khangura RS, Baireddy S, Yang C, Sparks EE, Dilkes B, Delp EJ, & Iyer?Pascuzzi AS. 2023. Image?based assessment of plant disease progression identifies new genetic loci for resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum in tomato. TPJ. 113(5): 887–903. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.16101
Mooney DF, Swinton SM, Subía C, & Peralta E. 2022. Returns to disease resistance research when pest management is an option. Sustainability. 14(5): 2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052859
My PDT, Tien LTT, Nga LP, Ngoc TH, Phuc VT, & Hoang HA. 2024. Efficacy of bacteriophage L522 against bacterial leaf blight of rice in Vietnam. J Appl Biol & Biotechnol. 12(2): 259–263. https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2024.158372
Nanayakkara D, Edirisingha I, Dissanayake L, Weerasinghe D, Suriyagoda L, Herath V, Perera C, & Jayatilake D. 2020. A novel intragenic marker targeting the ectodomain of bacterial blight-resistance gene Xa21 for marker-assisted selection in rice. J. Crop Improv. 34(6): 824–841. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427528.2020.1771643
Naveenkumar R, Anandan A, Singh V, Prabhukarthikeyan SR, Parameswaran C, Sangeetha G, Mahender A, Keerthana U, Singh PK, Patra BC, & Ali J. 2022. Deciphering environmental factors and defense response of rice genotypes against sheath blight disease. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 122: 101916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2022.101916
Nihad SAI, Ara A, Rashid MM, Hasan MAI, Khan MAI, & Latif MA. 2021. Genetic divergence of rice genotypes revealed by bacterial blight disease and morphological traits. Bangladesh Rice J. 24(1): 73–84. https://doi.org/10.3329/brj.v24i1.53241
Plank JE Van Der. 1963. Plant Diseases: Epidemics and Control. Academic Press, Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2013-0-11642-X
Rachmawati A, Suprihadi A, & Kusdiyantini DE. 2017. Identifikasi senyawa bioaktif pada isolat bakteri buah belimbing wuluh (Averrhoa bilimbi L.) sebagai agensia hayati Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae [Identification of bioactive compounds in bacterial isolates of the wuluh star fruit (Averrhoa bilimbi L.) as biological agents of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae]. Jurnal Akademika Biologi. 6(3): 1–11.
Rifki M, Hanifianto L, Juliastuti SR, Darmawan R, & Hendrianie N. 2018. Making organic fertilizer resistant to bacterial leaf blight disease for grain crops. MATEC Web Conf. 156: 03026. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201815603026
Rodrigues GB, Sobrinho GGR, Mituti T, Filho AB, Amorim L, Rezende JAM, & de Novaes QS. 2019. Etiology, occurrence and epidemiology of a begomovirus disease in passionflower in the southwest of Bahia. Sci. Agric. 76(4): 337–343. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-992x-2017-0272
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E, Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, Preibisch S, Rueden C, Saalfeld S, Schmid B, Tinevez JY, White DJ, Hartenstein V, Eliceiri K, Tomancak P, & Cardona A. 2012. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods. 9: 676–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019
Seshu DV. 1989. Salient findings from the multilocation evaluation of the international rice bacterial blight nursery. In: Banta SJ & Mew ECTW (Eds.). Proceedings of the International Workshop on Bacterial Blight of Rice. pp. 167-176. International Rice Research Institute.
Shi T, Guo X, Zhu J, Hu L, He Z, & Jiang D. 2021. Inhibitory effects of Carbazomycin B produced by Streptomyces roseoverticillatus 63 against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Front. Microbiol. 12: 616937. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.616937
Soesanto L, Nuraini IV, Sastyawan MWR, Mugiastuti E, Leana NWA, & Rahayuniati RF. 2024. Application of Bio P60 and Bio T10 alone or in combination to control fusarium wilt of hydroponic melon. J. Trop. Plant Pests Dis. 24(2): 199–211. https://doi.org/10.23960/jhptt.224199-211
Suryaningsih AS, Triwidodo H, & Wiyono S. 2023. Ketahanan enam galur padi asal petani terhadao penyakit hawar daun bakteri (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae [Resistance of six lines from farmers against bacterial leaf blight (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae)]. Jurnal Fitopatologi Indonesia. 19(4): 176–181. https://doi.org/10.14692/jfi.19.4.176-181
Vettori D & Rice SP. 2020. Implications of environmental conditions for health status and biomechanics of freshwater macrophytes in hydraulic laboratories. J. Ecohydraul. 5(1): 71–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/24705357.2019.1669496
Yuliani D & Sudir. 2022. Ketahanan galur padi IRBB terhadap penyakit hawar daun bakteri di Kabupaten Purwakarta dan Subang [Resistance of IRBB rice varieties to bacterial leaf blight in Purwakarta and Subang Districts]. Jurnal Agrowastagi. 10(2): 71–83.
Zander KK, Blaise P, & Holm-Müller K. 2023. Assessing German farmers’ trade-offs between disease resistance and yield in winter wheat varieties. Outlook Agric. 52(1): 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1177/00307270221140572
Zhang XB, Feng BH, Wang HM, Xu X, Shi YF, He Y, Chen Z, Sathe AP, Shi L, & Wu JL. 2018. A substitution mutation in OsPELOTA confers bacterial blight resistance by activating the salicylic acid pathway. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 60(2): 160–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12613