Molecular identification and characterization of Maconellicoccus multipori (Takahashi) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) on Piper nigrum L.
Main Article Content
Abstract
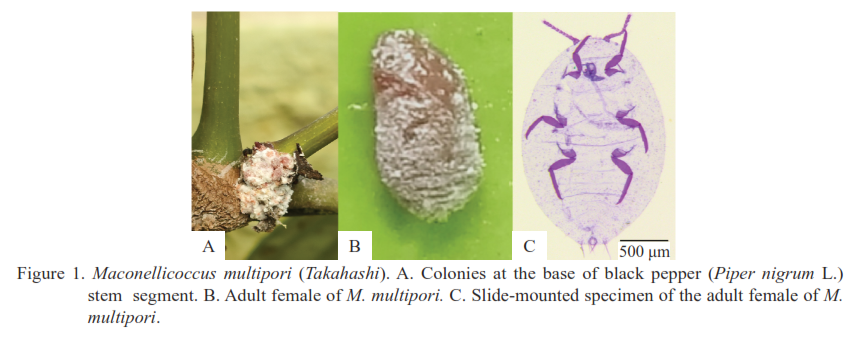
The mealybug Maconellicoccus multipori (Takahashi) was identified on black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) seedlings in a greenhouse in Bogor, West Java, using both molecular and morphological characterization. Two mealybug isolates were successfully amplified with primer pairs targeting the LCO region of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I (COI) gene, yielding a 491 bp PCR product. The nucleotide sequences of both isolates (GenBank accession numbers LC666906 and LC666907) were identical. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the Bogor isolates clustered closely with M. multipori populations from China and Thailand, with high sequence homology of 99.30% and 99.10%, respectively. Morphological observations of the adult female specimens further confirmed their identity as M. multipori, based on key diagnostic features including body size, antennal segmentation, cerarii pattern, and distribution of pores and ducts, which correspond to descriptions in established taxonomic keys. This study provides the first molecular characterization of M. multipori in Indonesia. The COI sequence data obtained enhances reference databases for DNA barcoding and strengthens early detection strategies for pest monitoring. These findings are crucial for supporting quarantine inspections, management, and control of M. multipori in black pepper nurseries and preventing its spread to other crops.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, & Lipman DJ. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215(3): 403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Balfas R, Supriadi, Mardiningsih TL, & Sugandi E. 2002. Penyebab dan serangga vektor penyakit keriting pada tanaman lada [The cause and insect vector of stunting disease of black pepper]. J. Littri. 8(1): 7–11.
Beltrà A, Soto A, & Malausa T. 2012. Molecular and morphological characterization of Pseudococcidae surveyed on crops and ornamental plants in Spain. Bul. Entomol. Res. 102(2): 165–172. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485311000514
Halima-Kamel MB, Germain JF, & Mdellel L. 2015. First records of two mealybugs, Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Green) and Phenacoccus peruvianus Granara de Willink, in Tunisia and the North of Africa. Bulletin OEPP/EPPO Bulletin. 45(1): 139–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/epp.12186
Devasahayam S. 2000. Insect pests of black pepper. In: Ravindran PN (Ed.). Black Pepper Piper nigrum. pp. 309–334. CRC Press, London. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203303870
García-Morales M, Denno BD, Miller DR, Miller GL, Ben-Dov Y, & Hardy NB. 2016. ‘ScaleNet: a literature-based model of scale insect biology and systematics’. http://scalenet.info/scalesplace/indonesia/. Accessed 19 June 2024.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, & Tamura K. 2018. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 35(6): 1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Malausa T, Fenis A, Warot S, Germain JF, Ris N, Prado E, Botton M, Vanlerberghe-Masutti F, Sforza R, Cruaud C, Couloux A, & Kreiter P. 2011. DNA markers to disentangle complexes of cryptic taxa in mealybugs (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). J. App. Entomol. 135(1–2): 142–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0418.2009.01495.x
Mazzeo G, Russo A, & Suma P. 1999. Phenacoccus solani Ferris (Homoptera Coccoidea) on ornamental plants in Italy. Boll. Zool. agr. Bachic. 31(1): 31–35.
Miftakhurohmah, Hidayat SH, Mutaqin KH, Soekarno BPW, & Wahyuno D. 2022a. Study on Ferrisia virgata and Planococcus minor as vectors of mottle disease in black pepper. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 974: 012030. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/974/1/012030
Miftakhurohmah, Hidayat SH, Mutaqin KH, Soekarno BPW, & Wahyuno D. 2022b. Identification of mealybugs on Piper nigrum as vector of piper yellow mottle virus (Badnavirus: Caulimoviridae). J. Trop. Plant Pest Dis. 22(2): 144–153. https://doi.org/10.23960/jhptt.222144-153
Miller DR. 1999. Identification of the pink hibiscus mealybug, Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Green) (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha: Pseudococcidae. Insecta Mundi. 13(3–4): 189–203.
Morales GM, Denno BD, Miller DR, Miller GL, Ben-Dov Y, & Hardy NB. 2016. ScaleNet: A literature-based model of scale insect biology and systematics. Database. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bav118. http://scalenet.info
Pellizzari G. 2005. Cocciniglie nuove o poco note potenzialmente dannose per l’Italia: Fiorina pinicola Maskell, Pseudococcus comstocki (Kuwana), Peliococcus turanicus (Kiritshenko). L’Informatore Fitopatologico. 55(6): 20–25.
Ren JM, Ashfaq M, Hu XN, Ma J, Liang F, Hebert PDN, Lin L, Germain JF, & Ahmed MZ. 2018. Barcode index numbers expedite quarantine inspections and aid the interception of nonindigenous mealybugs (Pseudococcidae). Biol. Invasions. 20: 449–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-017-1546-6
Rohimatun, Rahmah NN, Sartiami D, Aisyah MDN, Miftakhurohmah, Melati, Rusmin D, & Mardiningsih TL. 2024. Invasive mealybug Pseudococcus jackberadsleyi Gimpel and Miller on Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb. on the seed rhizome in storage: a record of a new host. J. Plant Prot. Res. 64(4): 298–306. https://doi.org/10.24425/jppr.2024.152883
Sartiami D, Sosromarsono S, Buchori D, & Suryobroto B. 1999. Keragaman spesies kutu putih pada tanaman buah-buahan di daerah Bogor [Diversity of mealybug species on fruit plants in Bogor area]. In: Prasadja I, Arifin M, Trisawa IM, Laba IW, Wikardi EA, Soetopo D, Wiratno, & Karmawati E (Eds.). Prosiding Seminar Nasional Peranan Entomologi dalam Pengendalian Hama yang Ramah Lingkungan dan Ekonomis. pp. 429–435. Perhimpunan Entomologi Indonesia. Bogor.
Sartiami D, Sihombing ER, & Balfas R. 2008. Identifikasi spesies kutu putih (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) pada tanaman lada (Piper nigrum LINN.) [Identification of mealybug species (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) on black pepper (Piper nigrum LINN)]. In: Sutrisno H, Peggie D, Nurdjito WA, Ratna ES, Kusumawati U, Gunandini D, Harnoto, Sukartana P, Pudjianto, Dadang, Laba IW, Winasa IW, Harahap IS, Kartohardjono A, Samudra IM, Koswanudin D, & Yuniawati R (Eds.). Prosiding Seminar Nasional V Pemberdayaan Keanekaragaman Serangga untuk Peningkatan Kesejahteraan Masyarakat. pp. 217–227. Perhimpunan Entomologi Indonesia. Bogor.
Wang XB, Zhang JT, Deng J, Zhou QS, Zhang YZ, & Wu SA. 2016. DNA barcoding of mealybugs (Hemiptera: Coccoidea: Pseudococcidae) from Mainland China. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 109(3): 438–446. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/saw009
Williams DJ. 1996. A brief account of the hibiscus mealybug Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), a pest of agriculture and horticulture, with descriptions of two related species from southern Asia. Bull. Entomol. Res. 86(5): 617–628. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485300039420
Williams DJ. 2004. Mealybugs of Southern Asia. The Natural History Museum, Southdene. Kuala Lumpur.
Williams DJ & Watson GW. 1988. The Scale Insects of the Tropical South Pacific Region. Part 2. The Mealybugs (Pseudococcidae) CAB International. Wallingford.
Zarkani A, Apriyanto D, Turanli F, Ercan C, & Kaydan MB. 2021. A checklist of Indonesian scale insects (Hemiptera: Coccomorpha). Zootaxa, 5016(2): 151?195. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5016.2.1